
Functional group
แปะเอกสารอ่าน
ผู้เข้าชมรวม
527
ผู้เข้าชมเดือนนี้
5
ผู้เข้าชมรวม
527
เนื้อเรื่อง
คืนค่าการตั้งค่าทั้งหมด
คุณแน่ใจว่าต้องการคืนค่าการตั้งค่าทั้งหมด ?
Table of common functional groups
The following is a list of common functional groups.[3] In the formulas, the symbols R and R' usually denote an attached hydrogen, or a hydrocarbon side chain of any length, but may sometimes refer to any group of atoms.
Hydrocarbons[edit]
Functional groups, called hydrocarbyl, that contain only carbon and hydrogen, but vary in the number and order of double bonds. Each one differs in type (and scope) of reactivity.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formulae | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkane | Alkyl | R(CH2)nH | alkyl- | -ane |  Ethane | |
| Alkene | Alkenyl | R2C=CR2 | 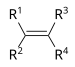 | alkenyl- | -ene | 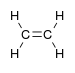 Ethylene (Ethene) |
| Alkyne | Alkynyl | RC≡CR' | alkynyl- | -yne | Acetylene (Ethyne) | |
| Benzene derivative | Phenyl | RC6H5 RPh | phenyl- | -benzene |  Cumene (2-phenylpropane) |
There are also a large number of branched or ring alkanes that have specific names, e.g., tert-butyl, bornyl, cyclohexyl, etc. Hydrocarbons may form charged structures: positively charged carbocations or negative carbanions. Carbocations are often named -um. Examples are tropylium and triphenylmethyl cations and thecyclopentadienyl anion.
Groups containing halogens
Haloalkanes are a class of molecule that is defined by a carbon–halogen bond. This bond can be relatively weak (in the case of an iodoalkane) or quite stable (as in the case of a fluoroalkane). In general, with the exception of fluorinated compounds, haloalkanes readily undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions or elimination reactions. The substitution on the carbon, the acidity of an adjacent proton, the solvent conditions, etc. all can influence the outcome of the reactivity.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| haloalkane | halo | RX | halo- | alkylhalide | Chloroethane (Ethyl chloride) | |
| fluoroalkane | fluoro | RF | fluoro- | alkylfluoride |  Fluoromethane (Methyl fluoride) | |
| chloroalkane | chloro | RCl | chloro- | alkylchloride |  Chloromethane (Methyl chloride) | |
| bromoalkane | bromo | RBr | bromo- | alkylbromide |  Bromomethane (Methyl bromide) | |
| iodoalkane | iodo | RI | iodo- | alkyliodide |  Iodomethane (Methyl iodide) |
Groups containing oxygen
Compounds that contain C-O bonds each possess differing reactivity based upon the location and hybridization of the C-O bond, owing to the electron-withdrawing effect of sp-hybridized oxygen (carbonyl groups) and the donating effects of sp2-hybridized oxygen (alcohol groups).
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | Hydroxyl | ROH |  | hydroxy- | -ol |  Methanol |
| Ketone | Carbonyl | RCOR' | 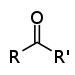 | -oyl- (-COR') or oxo- (=O) | -one |  Butanone (Methyl ethyl ketone) |
| Aldehyde | Aldehyde | RCHO |  | formyl- (-COH) or oxo- (=O) | -al |  Acetaldehyde (Ethanal) |
| Acyl halide | Haloformyl | RCOX |  | carbonofluoridoyl- carbonochloridoyl- carbonobromidoyl- carbonoiodidoyl- | -oyl halide | 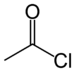 Acetyl chloride (Ethanoyl chloride) |
| Carbonate | Carbonate ester | ROCOOR | (alkoxycarbonyl)oxy- | alkyl carbonate | Triphosgene (bis(trichloromethyl) carbonate) | |
| Carboxylate | Carboxylate | RCOO− | 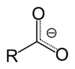 | carboxy- | -oate | Sodium acetate (Sodium ethanoate) |
| Carboxylic acid | Carboxyl | RCOOH |  | carboxy- | -oic acid |  Acetic acid (Ethanoic acid) |
| Ester | Ester | RCOOR' | 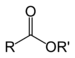 | alkanoyloxy- or alkoxycarbonyl | alkyl alkanoate | Ethyl butyrate (Ethyl butanoate) |
| Methoxy | Methoxy | ROCH3 | methoxy- | |||
| Hydroperoxide | Hydroperoxy | ROOH | hydroperoxy- | alkylhydroperoxide | tert-Butyl hydroperoxide | |
| Peroxide | Peroxy | ROOR |  | peroxy- | alkyl peroxide | Di-tert-butyl peroxide |
| Ether | Ether | ROR' | alkoxy- | alkyl ether | Diethyl ether (Ethoxyethane) | |
| Hemiacetal | Hemiacetal | RCH(OR')(OH) |  | alkoxy -ol | -al alkylhemiacetal | |
| Hemiketal | Hemiketal | RC(ORʺ)(OH)R' |  | alkoxy -ol | -one alkylhemiketal | |
| Acetal | Acetal | RCH(OR')(OR") | 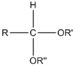 | dialkoxy- | -al dialkyl acetal | |
| Ketal (orAcetal) | Ketal (orAcetal) | RC(ORʺ)(OR‴)R' | 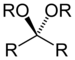 | dialkoxy- | -one dialkylketal | |
| Orthoester | Orthoester | RC(OR')(ORʺ)(OR‴) |  | trialkoxy- | ||
| Heterocycle | Methylenedioxy | PhOCOPh |  | methylenedioxy- | -dioxole |  1,2-Methylenedioxybenzene (1,3-Benzodioxole) |
| Orthocarbonate ester | Orthocarbonate ester | C(OR)(OR')(ORʺ)(OR″) | tetralkoxy- | tetraalkylorthocarbonate |
Groups containing nitrogen
Compounds that contain nitrogen in this category may contain C-O bonds, such as in the case of amides.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amide | Carboxamide | RCONR2 | 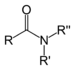 | carboxamido- or carbamoyl- | -amide |  Acetamide (Ethanamide) |
| Amines | Primary amine | RNH2 | amino- | -amine | 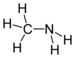 Methylamine (Methanamine) | |
| Secondary amine | R2NH |  | amino- | -amine | Dimethylamine | |
| Tertiary amine | R3N | 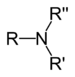 | amino- | -amine | 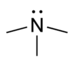 Trimethylamine | |
| 4° ammonium ion | R4N+ | 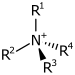 | ammonio- | -ammonium |  Choline | |
| Imine | Primary ketimine | RC(=NH)R' |  | imino- | -imine | |
| Secondary ketimine |  | imino- | -imine | |||
| Primary aldimine | RC(=NH)H |  | imino- | -imine | Ethanimine | |
| Secondary aldimine | RC(=NR')H |  | imino- | -imine | ||
| Imide | Imide | (RCO)2NR' |  | imido- | -imide |  Succinimide (Pyrrolidine-2,5-dione) |
| Azide | Azide | RN3 | azido- | alkyl azide |  Phenyl azide (Azidobenzene) | |
| Azo compound | Azo (Diimide) | RN2R' |  | azo- | -diazene |  Methyl orange (p-dimethylamino-azobenzenesulfonic acid) |
| Cyanates | Cyanate | ROCN | cyanato- | alkyl cyanate |  Methyl cyanate | |
| Isocyanate | RNCO | isocyanato- | alkylisocyanate | Methyl isocyanate | ||
| Nitrate | Nitrate | RONO2 | nitrooxy-, nitroxy- | alkyl nitrate |  Amyl nitrate (1-nitrooxypentane) | |
| Nitrile | Nitrile | RCN | cyano- | alkanenitrile alkyl cyanide |  Benzonitrile (Phenyl cyanide) | |
| Isonitrile | RNC | isocyano- | alkaneisonitrile alkyl isocyanide | Methyl isocyanide | ||
| Nitrite | Nitrosooxy | RONO | nitrosooxy- | alkyl nitrite |  Isoamyl nitrite (3-methyl-1-nitrosooxybutane) | |
| Nitro compound | Nitro | RNO2 |  | nitro- |  Nitromethane | |
| Nitroso compound | Nitroso | RNO | nitroso- (Nitrosyl-) | Nitrosobenzene | ||
| Oxime | Oxime | RCH=NOH | 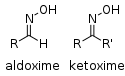 | Oxime |  Acetone oxime (2-Propanone oxime) | |
| Pyridine derivative | Pyridyl | RC5H4N | 4-pyridyl 3-pyridyl 2-pyridyl | -pyridine |  Nicotine |
Groups containing sulfur[edit]
Compounds that contain sulfur exhibit unique chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than oxygen, their lighter analogue on the periodic table. Substitutive nomenclature (marked as prefix in table) is preferred over functional class nomenclature (marked as suffix in table) for sulfides, disulfides, sulfoxides and sulfones.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thiol | Sulfhydryl | RSH |  | sulfanyl- (-SH) | -thiol | Ethanethiol |
| Sulfide (Thioether) | Sulfide | RSR' | substituent sulfanyl- (-SR') | di(substituent) sulfide | (Methylsulfanyl)methane (prefix) or Dimethyl sulfide (suffix) | |
| Disulfide | Disulfide | RSSR' | substituent disulfanyl- (-SSR') | di(substituent) disulfide | (Methyldisulfanyl)methane (prefix) or Dimethyl disulfide (suffix) | |
| Sulfoxide | Sulfinyl | RSOR' |  | -sulfinyl- (-SOR') | di(substituent) sulfoxide |  (Methanesulfinyl)methane (prefix) or Dimethyl sulfoxide (suffix) |
| Sulfone | Sulfonyl | RSO2R' |  | -sulfonyl- (-SO2R') | di(substituent) sulfone |  (Methanesulfonyl)methane (prefix) or Dimethyl sulfone (suffix) |
| Sulfinic acid | Sulfino | RSO2H | 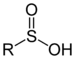 | sulfino- (-SO2H) | -sulfinic acid | 2-Aminoethanesulfinic acid |
| Sulfonic acid | Sulfo | RSO3H |  | sulfo- (-SO3H) | -sulfonic acid | 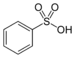 Benzenesulfonic acid |
| Thiocyanate | Thiocyanate | RSCN | thiocyanato- (-SCN) | substituent thiocyanate | 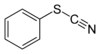 Phenyl thiocyanate | |
| Isothiocyanate | RNCS | isothiocyanato- (-NCS) | substituent isothiocyanate | Allyl isothiocyanate | ||
| Thione | Carbonothioyl | RCSR' |  | -thioyl- (-CSR') or sulfanylidene- (=S) | -thione | Diphenylmethanethione (Thiobenzophenone) |
| Thial | Carbonothioyl | RCSH |  | methanethioyl- (-CSH) or sulfanylidene- (=S) | -thial | |
| Thioester | ||||||
| carbodithioic acid |
Groups containing phosphorus[edit]
Compounds that contain phosphorus exhibit unique chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than nitrogen, their lighter analogues on the periodic table.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphine (Phosphane) | Phosphino | R3P |  | phosphanyl- | -phosphane | Methylpropylphosphane |
| Phosphonic acid | Phosphono | 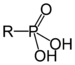 | phosphono- | substituentphosphonic acid | Benzylphosphonic acid | |
| Phosphate | Phosphate | 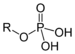 | phosphonooxy- or O-phosphono- (phospho-) | substituentphosphate | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (suffix) | |
O-Phosphonocholine (prefix) (Phosphocholine) | ||||||
| Phosphodiester | Phosphate | HOPO(OR)2 |  | [(alkoxy)hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy- or O-[(alkoxy)hydroxyphosphoryl]- | di(substituent) hydrogen phosphate or phosphoric acid di(substituent) ester | DNA |
| O‑[(2‑Guanidinoethoxy)hydroxyphosphoryl]‑l‑serine (prefix) (Lombricine) |
Groups containing boron[edit]
Compounds containing boron exhibit unique chemistry due to their having partially filled octets and therefore acting as Lewis acids.
| Chemical class | Group | Formula | Structural Formula | Prefix | Suffix | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boronic acid | Borono | RB(OH)2 |  | Borono- | substituent boronic acid |  Phenylboronic acid |
| Boronic ester | Boronate | RB(OR)2 |  | O-[bis(alkoxy)alkylboronyl]- | substituent boronic acid di(substituent) ester | |
| Borinic acid | Borino | R2BOH |  | Hydroxyborino- | di(substituent) borinic acid | |
| Borinic ester | Borinate | R2BOR | 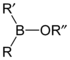 | O-[alkoxydialkylboronyl]- | di(substituent) borinic acid substituent ester |  Diphenylborinic acid 2-aminoethyl ester (2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate) |
Names of radicals or moieties[edit]
These names are used to refer to the moieties themselves or to radical species, and also to form the names of halides and substituents in larger molecules.
When the parent hydrocarbon is unsaturated, the suffix ("-yl", "-ylidene", or "-ylidyne") replaces "-ane" (e.g. "ethane" becomes "ethyl"); otherwise, the suffix replaces only the final "-e" (e.g. "ethyne" becomes "ethynyl").[4]
Note that when used to refer to moieties, multiple single bonds differ from a single multiple bond. For example, a methylene bridge (methanediyl) has two single bonds, whereas a methylene group (methylidene) has one double bond. Suffixes can be combined, as in methylidyne (triple bond) vs. methylylidene (single bond and double bond) vs. methanetriyl (three single bonds).
There are some retained names, such as methylene for methanediyl, 1,x-phenylene for phenyl-1,x-diyl (where x is 2, 3, or 4),[5] carbyne for methylidyne, and trityl for triphenylmethyl.
ผลงานอื่นๆ ของ Have_a_hope ดูทั้งหมด
ผลงานอื่นๆ ของ Have_a_hope
คำนิยม Top
ยังไม่มีคำนิยมของเรื่องนี้
คำนิยมล่าสุด
เขียนคำนิยมยังไม่มีคำนิยมของเรื่องนี้
















ความคิดเห็น